Extrusion compounding
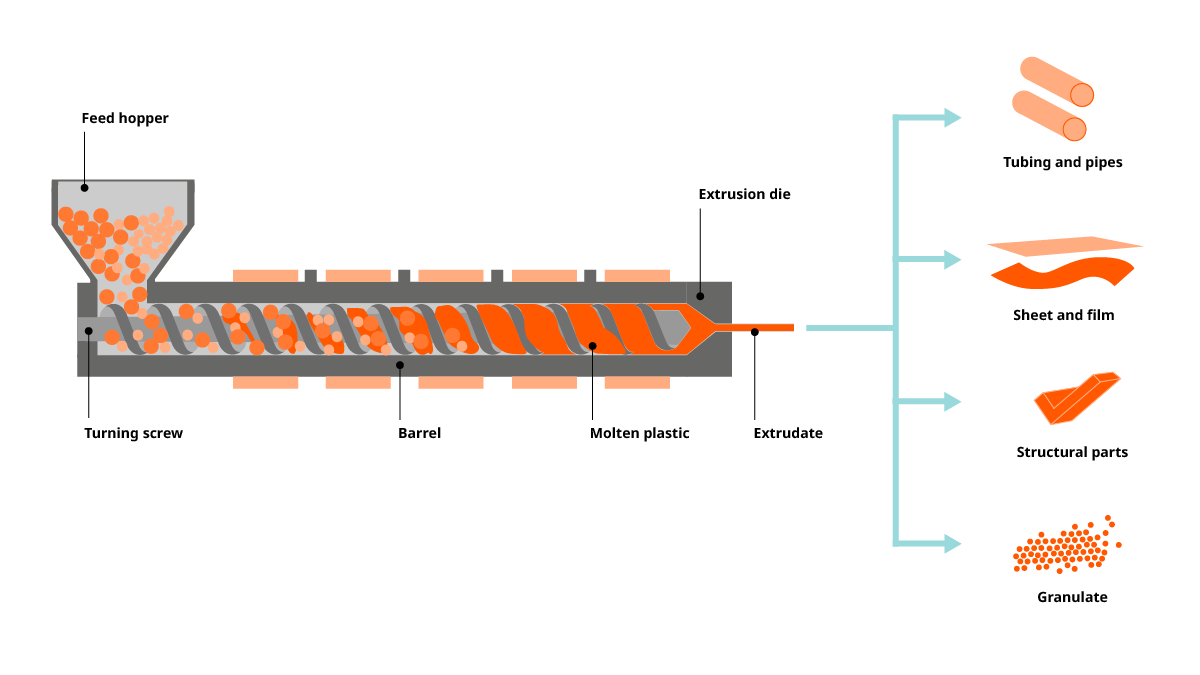
As well as manufacturing finished products, extruders can also be used to create new plastic compounds for further processing.
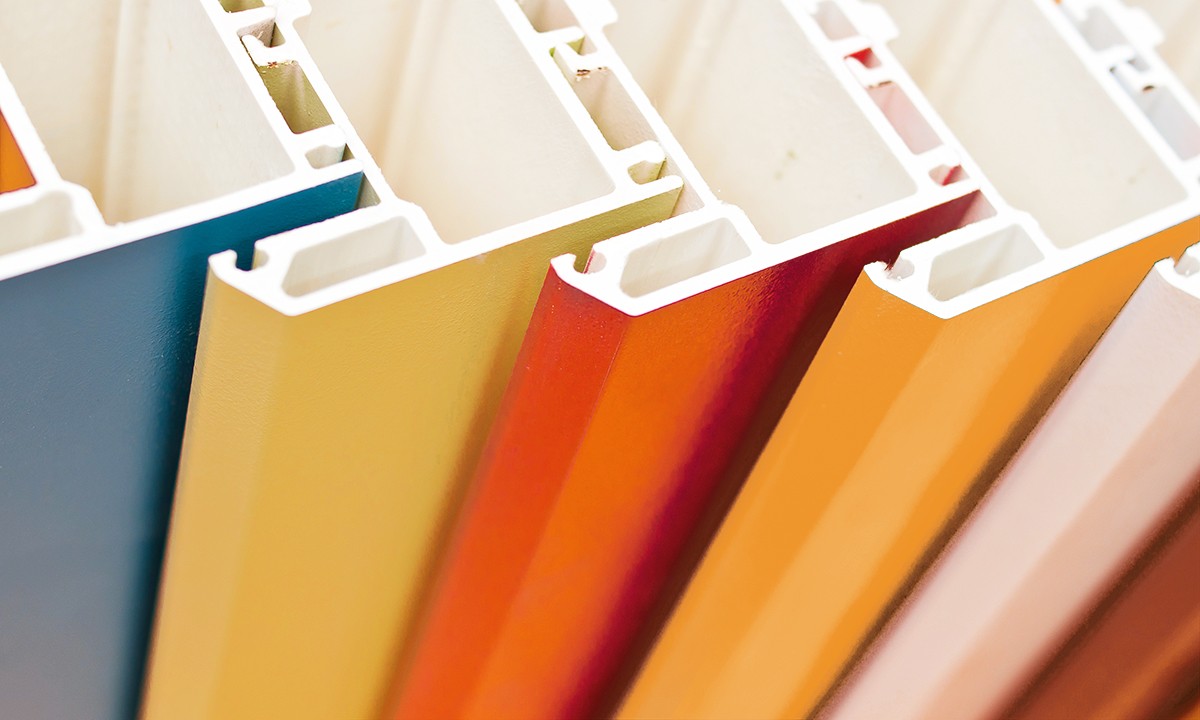
By mixing additives with the base material, the plastic can be given different properties. This can be for reasons of appearance, such as to make it a different color, or to give it different properties like extra strength, such as an extra-durable plastic for window and door frames.
These extra ingredients are added to the feed hopper along with the plastic pellets or granules. From here, the process is the same as a typical extrusion process: As they progress through the extruder, the ingredients melt and are mixed by the rotating screw. To ensure a homogenous product with no defects, this takes place under vacuum.
Then the molten plastic passes through the shaping die. However, rather than being formed into a complex shape, they are pushed through a die that creates thin, spaghetti-like strands, which can subsequently be cut into pellets. Vacuum not only aids in removing air bubbles and impurities but also ensures consistent pellet quality, which is essential for further processing.
These pellets can later be used in different plastic processes, such as injection molding or extrusion, to create a wide variety of products.
Matching products