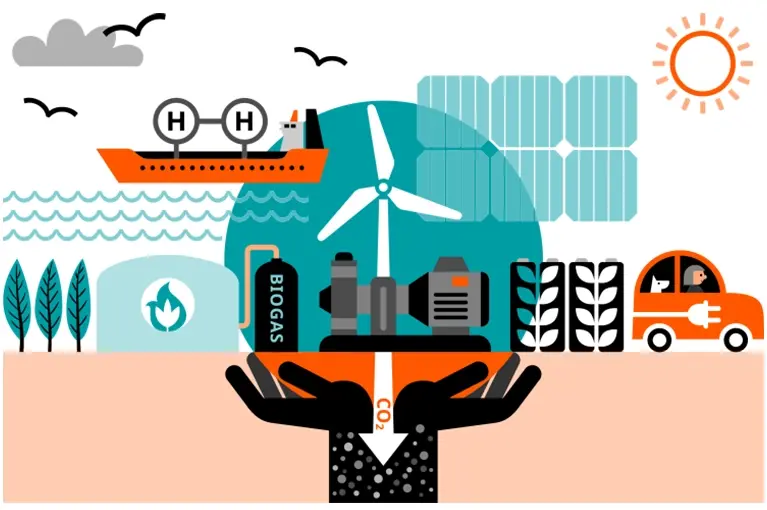
Burning fossil fuels in a conventional power plant releases enormous amounts of carbon dioxide every day. However, there is an alternative to discharging this directly into the air. Some power plants and other carbon-heavy industries are now investing in industrial carbon capture technology, limiting or even eliminating the carbon that they release into the atmosphere. This technology uses vacuum pumps to capture the CO
2.
Direct air capture (DAC) is an alternative method of carbon capture. Rather than being situated at the source of the CO
2, DAC extracts carbon dioxide straight from the ambient air. It can therefore be used as a complementary method to reduce the emissions that are already in our atmosphere, rather than preventing them from being released.
Whichever method is used, there are two options for the carbon dioxide once captured. The first is permanent storage. The CO
2 is mixed with water to create carbonic acid. Then it is pumped deep below the earth’s surface, where it reacts with the basalt bedrock, mineralizes and forms a solid.
The second option is to recycle the carbon dioxide. It can be used directly to stimulate plant growth in greenhouses, or for fire suppression. Or it can be used to create other chemicals, such as melamine, glue, or fertilizer.
Learn how Climeworks uses
direct air capture technology to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere:
Direct Air Capture