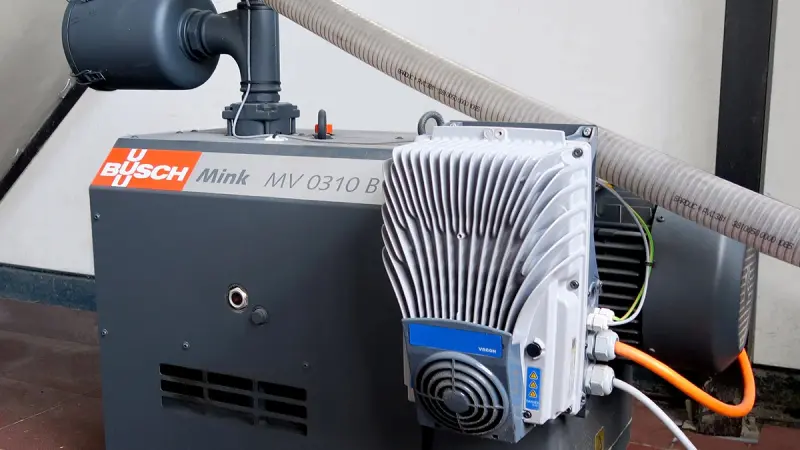
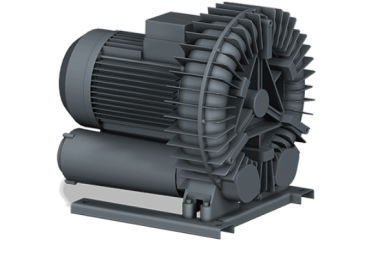
When you need air flow in your process, you have the choice between an air blower and a compressor. The difference is in the pressure: Compressors compact air into a small space, making the air denser. Air blowers, on the other hand, only move it by increasing the pressure slightly. As a result, the pressure ratio of a blower is much lower than that of a compressor, making them cheaper and more energy efficient to run. If you need a solution with higher pressure, you will find all relevant information about compressors.
Operating principle of air blowers
Put simply, blowers work by trapping air to increase its pressure, then releasing it. The exact operating principle depends on the type of blower.Types of industrial air blowers
Rotary lobe blowers
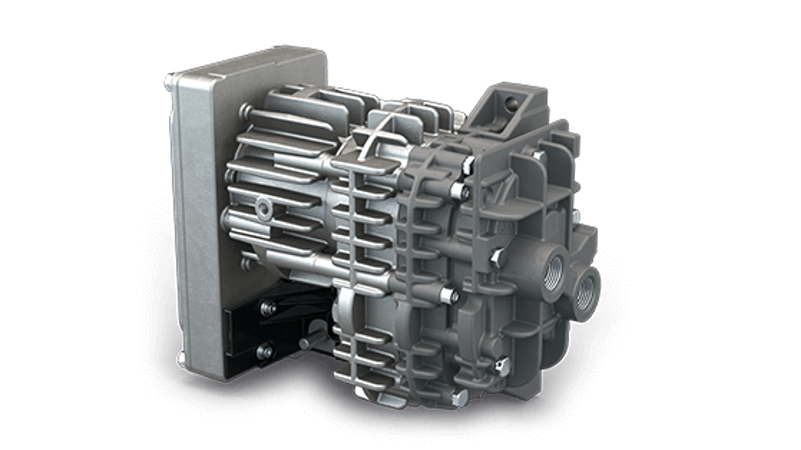
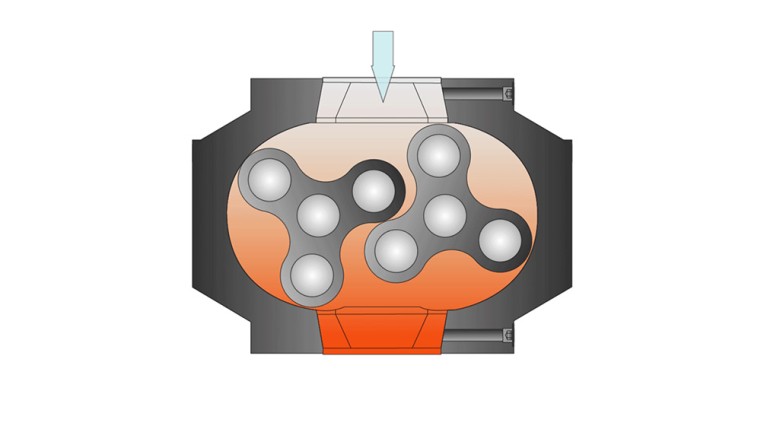
The rotary lobe blower is a type of positive displacement blower and operates according to the Roots principle. It produces a high air flow at a low pressure. Inside a cylindrical housing, two rotary lobes are mounted in parallel. These three-bladed lobes rotate in opposite directions. The rotation of the lobes traps the air or gas in the space between the rotors and the housing, then transports it to the outlet. There, the air is released, now at a higher pressure.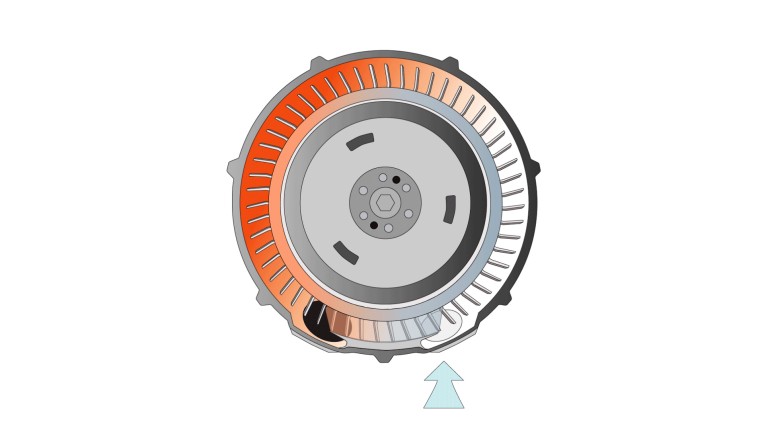
Side channel blowers
Side channel blowers transfer the kinetic energy of a rotating impeller to the air or gas and convert it into pressure. The impeller is mounted on the shaft of the motor. Together with the specially shaped housing, it forms the side channel.The air or gas is drawn into the side channel and compressed. Single-stage side channel blowers discharge it after one rotation. Two-stage versions convey it to the second stage after one rotation. Here, it is compressed again and discharged afterwards. This leads to higher differential pressures.
A side channel blower provides variable airflow at a lower pressure than a rotary lobe blower, but at a higher pressure than a fan.
Technical considerations for selecting air blowers
To decide which blower your process needs, a thorough analysis of your application is of the utmost importance. Key factors that should be considered are:
Flow and pressure
You should select a blower that produces only the pressure you need for your process. This reduces energy consumption and increases efficiency, thus giving lower operating costs than a blower or compressor that runs at a higher capacity.
Operating conditions
The conditions in which the blower will operate may influence your decision. Technology with a small footprint is ideal if there is little room on the production floor. And other factors, such as levels of dust, humidity, and heat, should also be taken into account.
Initial outlay vs. ROI
The lowest purchase price does not necessarily mean the lowest operating costs. When deciding which blower to purchase, you should consider both the initial investment and the operating costs over the blower’s life cycle to get the maximal return on investment. Energy efficiency can play a role here: Energy-efficient technology may require a higher initial outlay, but will result in lower long-term energy costs.
Noise levels
Where is the blower located in relation to people? Close proximity means the need for a quieter blower to maintain a comfortable working environment. Blowers from Busch have internal silencers, making them the ideal choice for an installation in the immediate vicinity of workstations. This also has a positive impact on installation costs: There is no need for specially soundproofed areas or long piping.
Service and support
How much servicing will your blower require and what levels of service do the manufacturers provide? Some older blower technologies may require units to be taken back to the manufacturer to be serviced, repaired, or refurbished. Long periods of downtime are the result. Blowers from Busch have low-maintenance components, such as lifetime-lubricated bearings and contact-free impellers. This ensures that annual servicing is minimal.Main uses for air blowers
Compressed air at a low pressure is needed for a variety of industrial applications. These include pneumatic conveying, wastewater treatment, and aquaculture:-
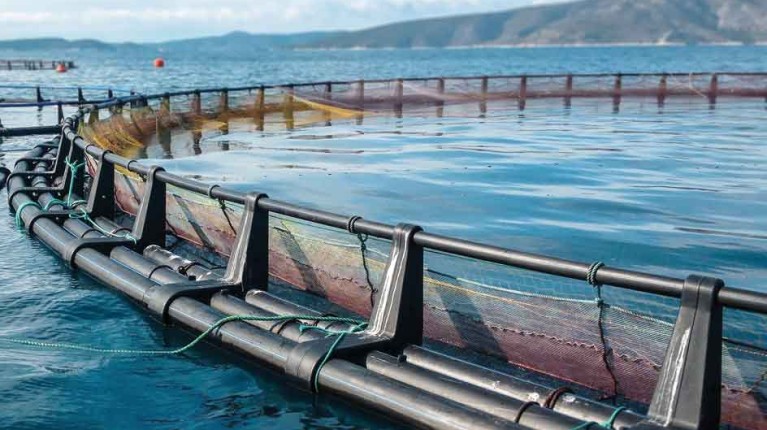
Aquaculture / Fish farming
The aquaculture industry uses blowers and compressors in a variety of different ways. They can be employed to maintain water quality, supply feeding systems, create bubble curtains, or to move stocks within the farm. Many of these processes require a blower that can provide pure, oil-free air.

-
Pneumatic conveying
Pneumatic conveying is used in many manufacturing processes to transport dry bulk materials or powders through a pipeline. Find out more.

-
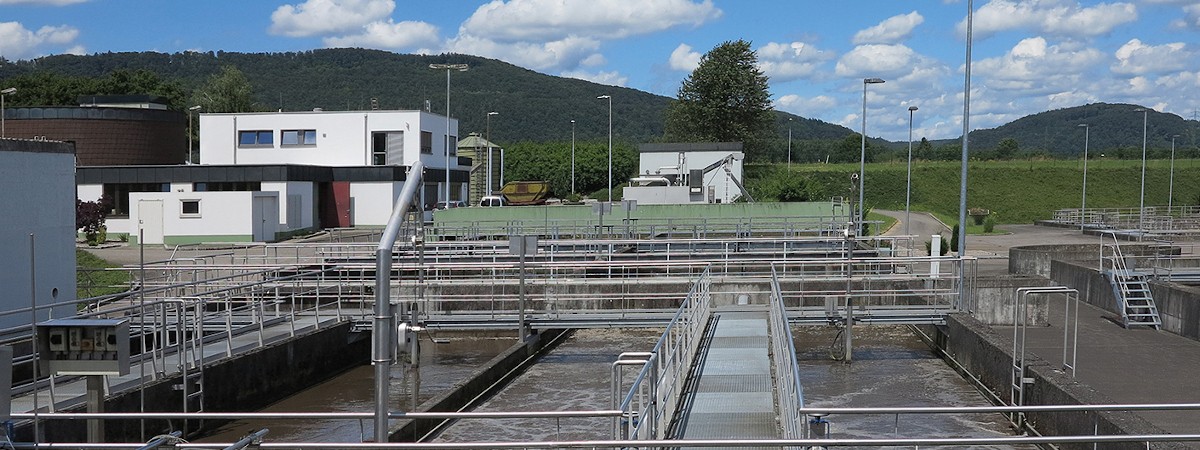
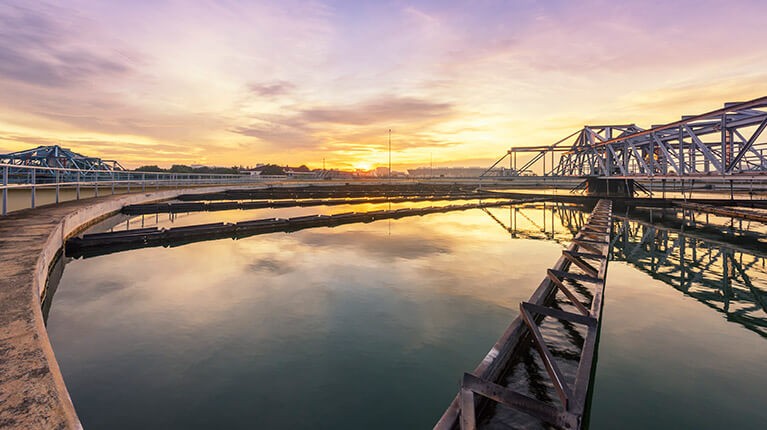
Wastewater treatment
Aerobic wastewater treatment plants use millions of living bacteria and microorganisms to treat organic waste, breaking it down into carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and clean water. These bacteria need a reliable and steady flow of oxygen to survive. The aeration tanks are supplied with this clean air through continuous blower operation.

-
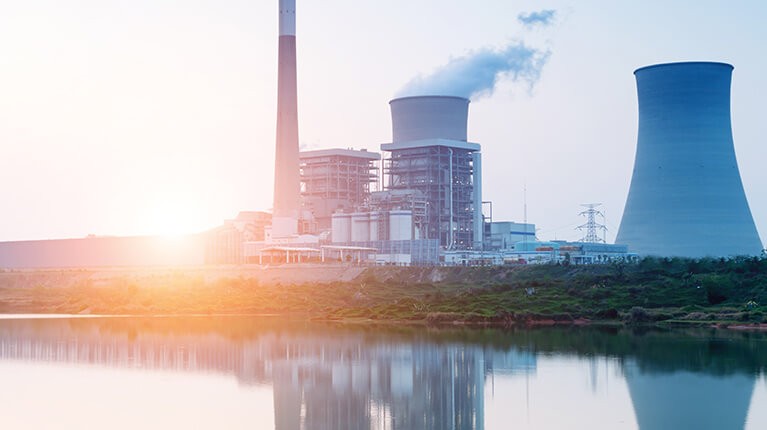
Flue gas desulfurization
Without the appropriate system in place, coal-fired power plants release harmful sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere. However, blowers can be used to remove it from the exhaust flue gases, reducing emissions and helping meet local standards for emission reduction. Blowers for this application are in operation around the clock, requiring machines that can operate with virtually zero downtime and a reliable, constant air supply.

FAQ
How do air blowers work?
Blowers work by increasing air pressure. The exact operating principle depends on the type of blower. A side channel blower transfers the kinetic energy of a rotating impeller to the air or gas and converts it into pressure. A rotary lobe blower operates differently. Two three-bladed lobes operate in opposite directions. The rotation of the lobes traps the air or gas, compresses it, and transports it to the next stage or the outlet.
What are aeration blowers?
Aeration blowers are used in wastewater treatment. They provide aeration to promote aerobic digestion and keep solids suspended in activated sludge tanks. There is no specific blower technology used for aeration: the name refers only to the blower application.
What are industrial blowers?
Industrial blowers are machines that provide a large flow of air or gas for a specific industrial application. This air is at a slightly higher pressure than ambient air and is concentrated in one specific direction. This name refers to the application, not a specific blower technology.
What is the difference between a fan and a blower?
Both fans and blowers circulate air. A fan moves air or gas with a very low increase in pressure, and usually circulates air throughout a wide area, such as a room. A blower, on the other hand, concentrates the air flow in one specific direction at a slightly higher pressure.
What is the difference between a compressor and blower?
While both a compressor and a blower create overpressure, they use different methods and give different results. A blower uses a slight increase in pressure to push the gas in a certain direction. A compressor raises the pressure of the gas by compressing it into a small space, making it denser.
What is the difference between a vacuum pump and a blower?
The difference is in the pressure. A blower is used when overpressure is needed (blowing), whereas a vacuum pump is used when suction is required.
What is the difference between a leaf blower and industrial and aeration blowers?
Leaf blowers and industrial blowers work on the same principle and use the same technology – only the way they are installed is different. Industrial and aeration blowers are permanently installed industrial equipment and may use any form of blower technology. A leaf blower is a type of centrifugal blower that has been specifically designed to move leaves in a garden or public space. It must therefore be portable, reasonably light, and simple to use.