Please update your browser.
It looks like you are using an old version of the Microsoft Edge browser. To get the best experience with the Busch website, please update your browser.
Please update your browser.
It looks like you are using an old version of the Microsoft Edge browser. To get the best experience with the Busch website, please update your browser.




Healthcare industry
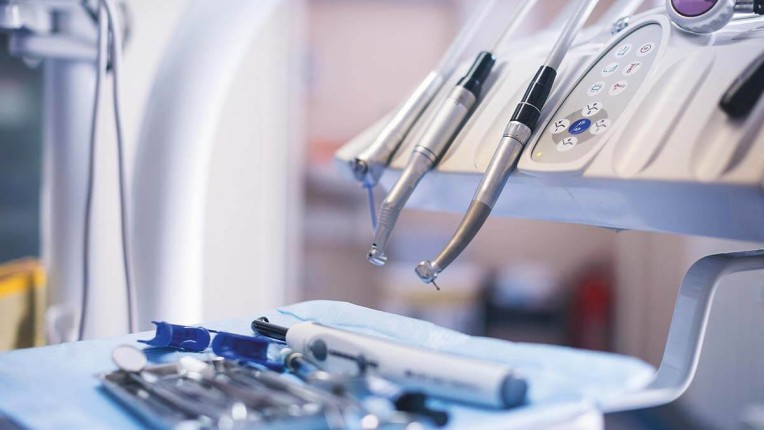
Compressed air is used in many different applications throughout hospitals and other medical facilities. Compressors generate breathing air for those with respiratory conditions, under anesthesia, or who need to inhale certain medications. Compressed air is also used to power surgical tools and equipment in the operating room. In dental procedures, compressors provide compressed air to power pneumatically operated dental instruments, such as drills or toothbrushes.

Biogas production
To create biogas, organic waste is broken down by microorganisms in an oxygen-free environment. Compressors are used in the recirculation process to increase the activity of these anaerobic bacteria and avoid sediment accumulating on the bottom of the tank. They also compress the biogas before it is injected into the natural gas network pipeline.

Pneumatic conveying
Pneumatic conveying is used in many manufacturing processes to transport dry bulk materials or powders through a pipeline. Find out more.

Printing industry
The printing industry uses compressed air for various processes, such as separating individual paper sheets and feeding them into the printing machine. Compressed air is also needed for such tools as pressers, rollers, and paper drills.

Controlled atmosphere ultra-low-oxygen storage
After harvest, fruits and vegetables can either be transported immediately, or stored for later. A controlled atmosphere in ultra-low-oxygen storage (CA/ULO) increases the storage time while maintaining the product’s original taste. Compressors are an integral part of the pressure swing adsorption (PSA) process, which generates the nitrogen necessary to create the optimal storage atmosphere.

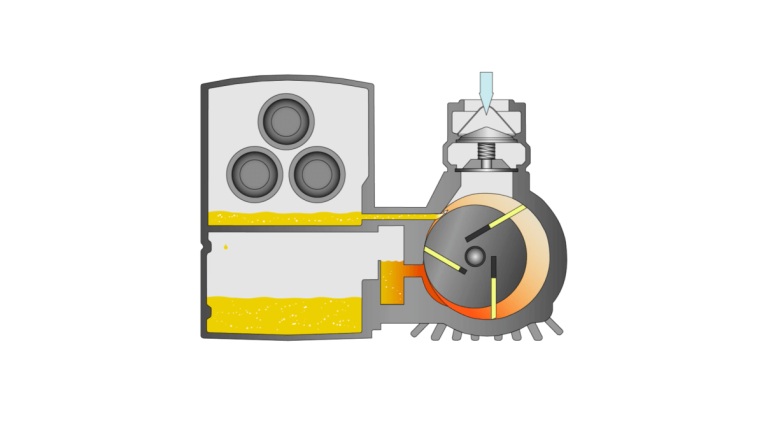
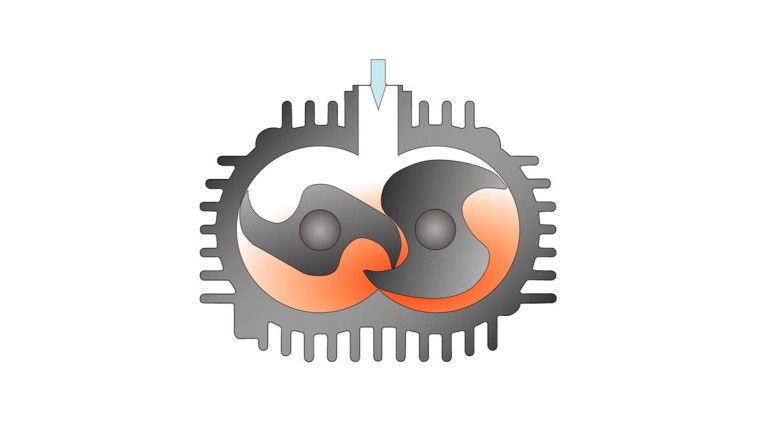
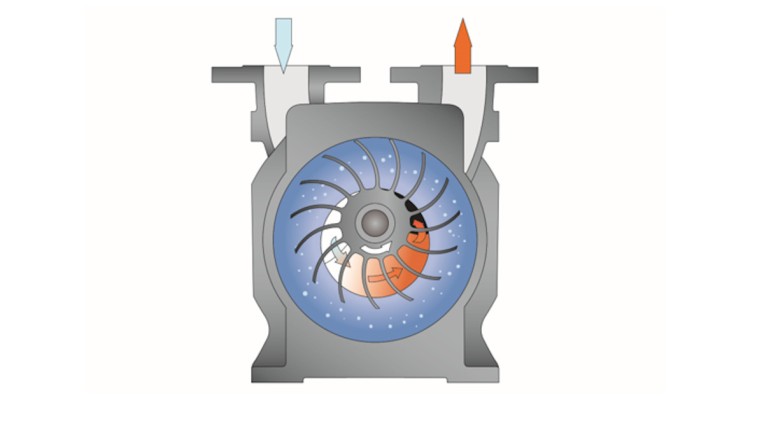
Air compressors compress air or gas, creating a high-pressure air flow. The exact operating principle varies depending on the technology, but a positive displacement air compressor pushes air through a chamber of gradually decreasing volume.
While both a compressor and a blower create overpressure, they use different methods and give different results. A blower uses a slight increase in pressure to push the air or gas in a certain direction. A compressor raises the pressure of the air or gas by compressing it into a small space, making it denser.
The operating principle is the main difference between a vacuum pump and a compressor. A vacuum pump draws air from a closed environment or container, creating vacuum. An air compressor draws air from the ambient environment and compresses it into a container with a high pressure. Put simply, a compressor fills a space with air, and a vacuum pump empties it.
The pressure you need is determined by how much force is needed to perform a certain task at a particular moment. Choose a compressor that does not generate enough pressure, and it will not be able to complete the task, but choose a compressor that generates more pressure than is needed, and energy will be wasted.
Flow refers to how well the compressor can carry out the task over a certain period. A lower flow is needed if a task is carried out intermittently than if it is continuous. For a continuously running process, the compressor must have adequate flow to avoid interruptions.
If you are uncertain what size of compressor is best for your application, get in touch with us . We will be happy to help.