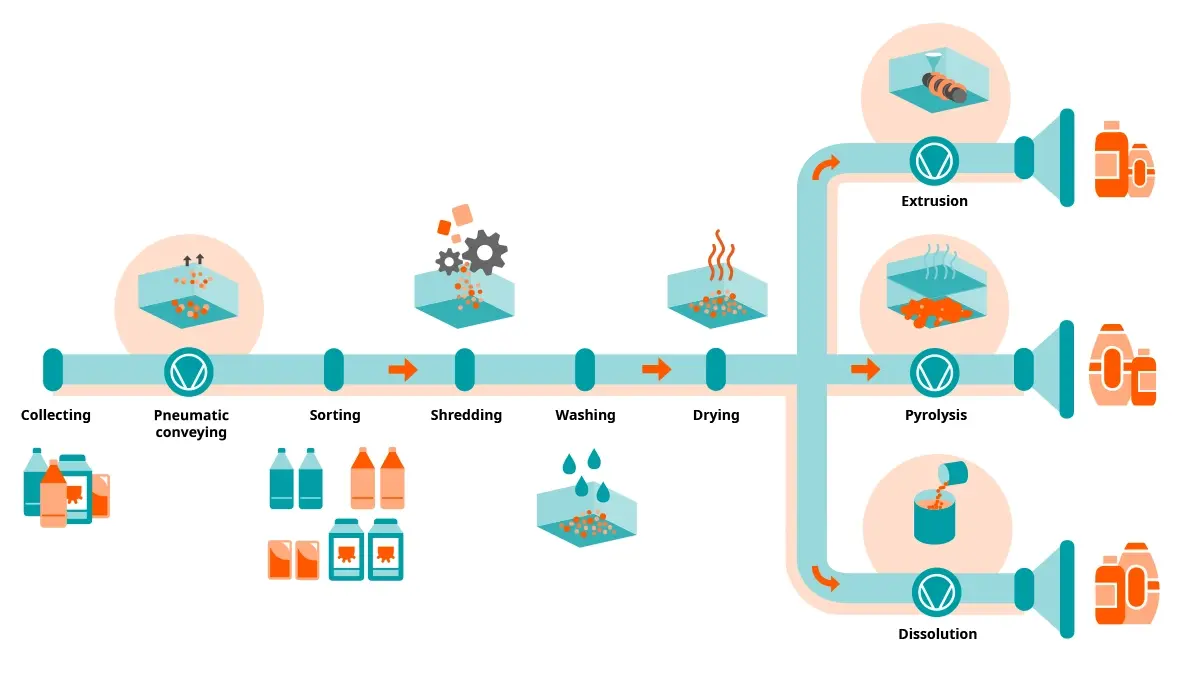
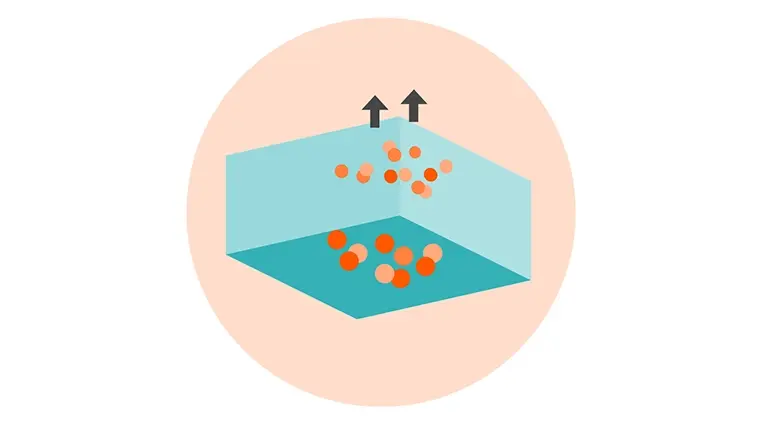
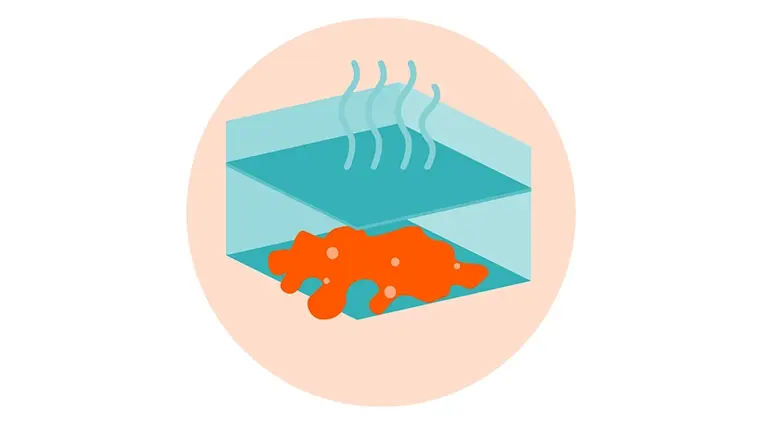
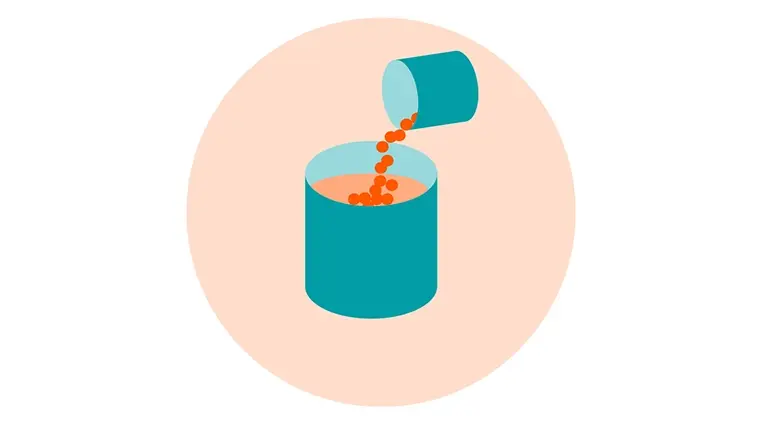
Giving plastics a new lease on life with vacuum
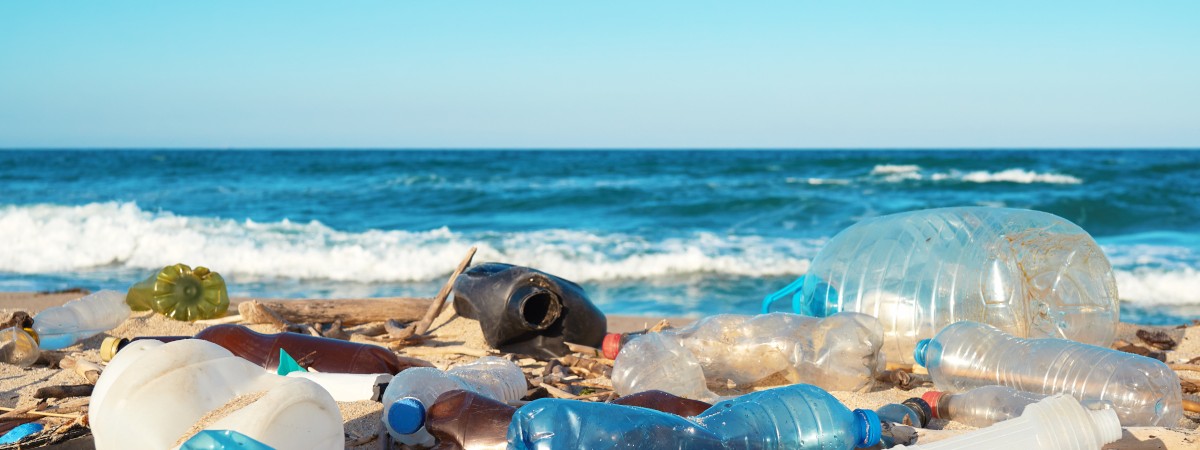
Plastic is a highly versatile material, popular in many industries today, from food packaging to industrial machinery. But it is also one of the most persistent pollutants on Earth.It takes over 400 years for plastics to break down. In the meantime, they find their way into the world’s oceans, contributing to the estimated 5.25 trillion pieces of debris they currently contain. And even then, they do not fully decompose. They wear down into microplastics that continue to pollute our environment and enter the food chain.
Plastic pollution is a global problem, which makes plastics recycling one of the most important actions towards sustainability. With reliable vacuum technology, plastics can be recycled to create new products. Keeping our world cleaner and giving plastics a longer useful life.