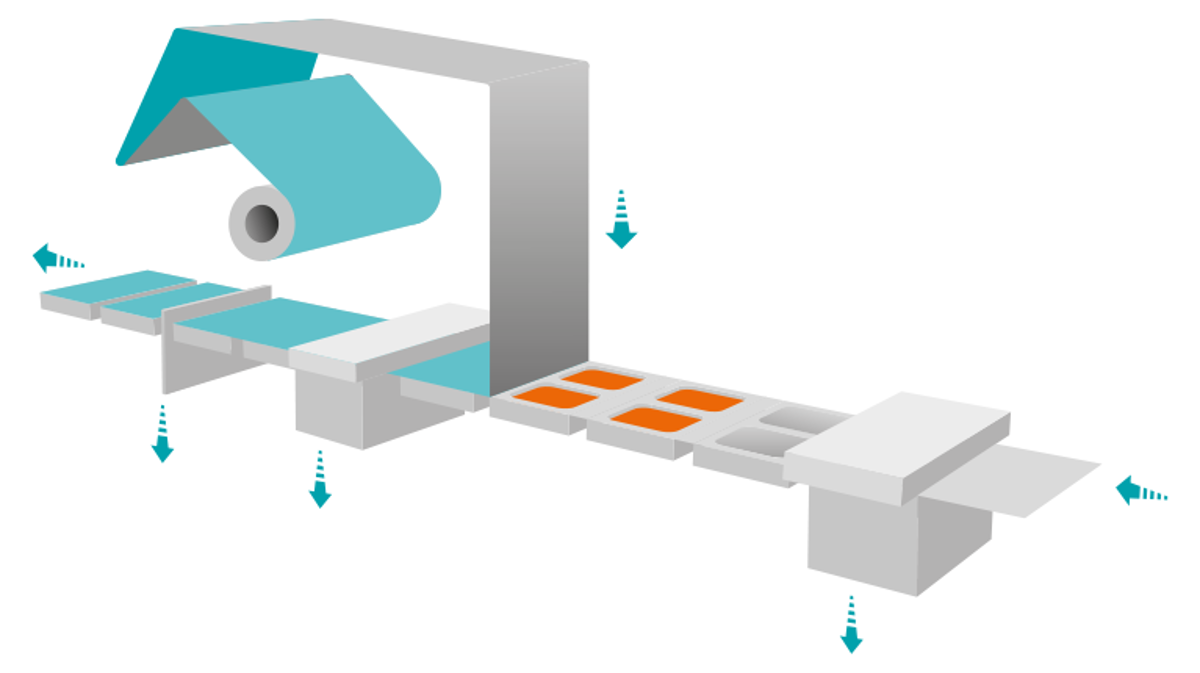
The role of vacuum in thermoforming
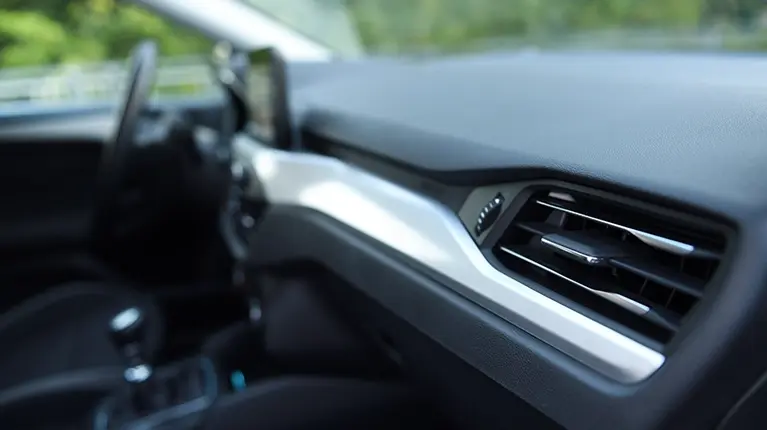
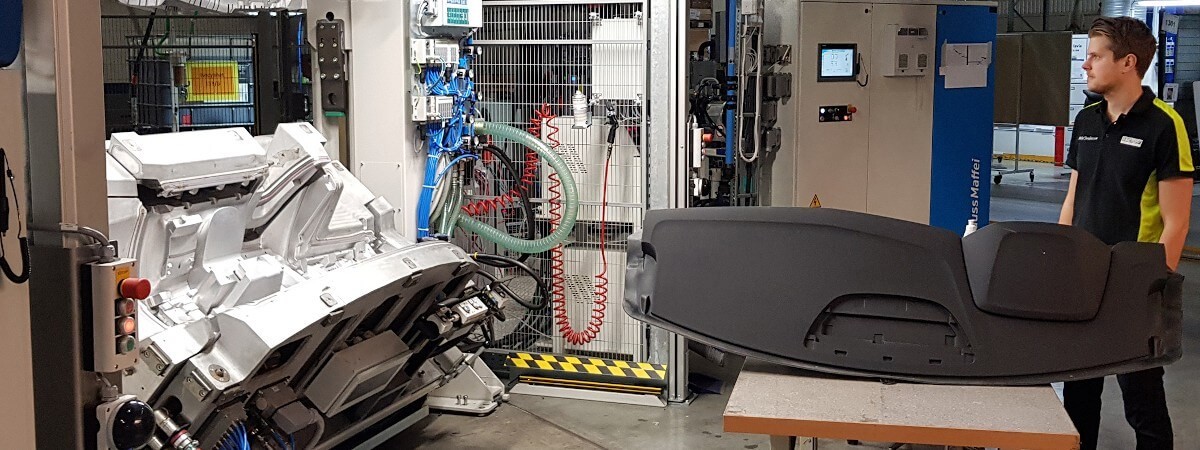
Thermoforming plastic is a method of reshaping plastic used in an enormous range of industries. By means of a mold, heat and vacuum, flat sheets of thermoplastic are transformed into three-dimensional objects. From car dashboards to syringes.First, a plastic sheet is heated until it becomes pliable. Then, it is shaped using a mold. Depending on the process, the plastic can either be laid over the mold (male/positive molding) or pulled into it (female/negative molding).